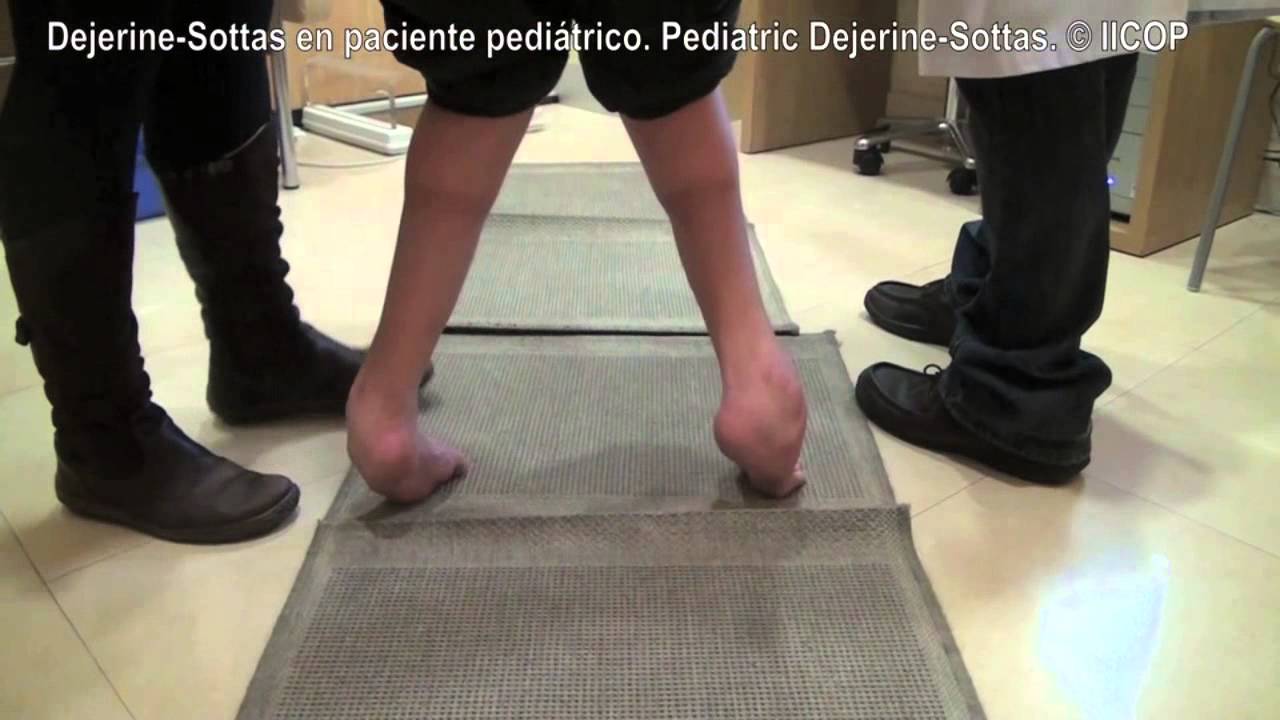
Dejerine-sottas Syndrome
Dejerine-sottas syndrome. Sometimes also described as a subtype III of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive neuropathy. It is also sometimes called type 3 CMT3. DejerineSottas syndrome is a hypertrophic demyelinating neuropathy which appears to demonstrate autosomal recessive inheritance in most pedigrees.
Peripheral nerves are the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. Some patients have generalized hypotonia in infancy. Dejerine-Sottas is a rare autosomal recessive condition with occasional sporadic cases that encompasses a particular constellation of.
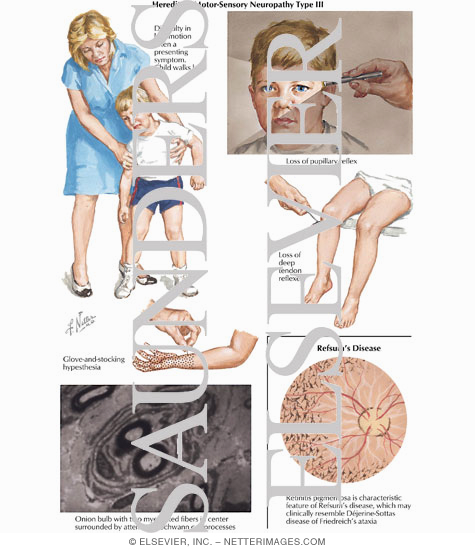
Déjerine-Sottas disease also known as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type III or hypertrophic interstitial polyneuritis is a rare hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy HMSN. DejerineSottas syndrome is a hypertrophic demyelinating neuropathy which appears to demonstrate autosomal recessive inheritance in most pedigrees. Unlike hearing loss vestibular loss is difficult to identify particularly in a patient presumed to.
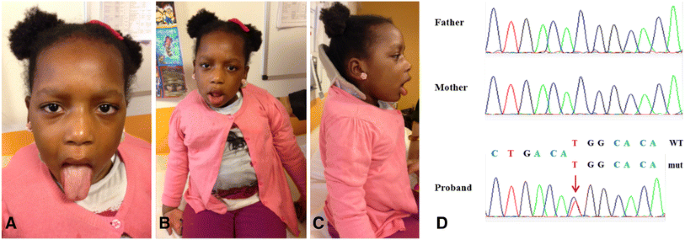
Clinical symptoms are similar but more severe than CharcotMarieTooth disease type 1 CMT1 of which the major subtype CMT1 A results either from duplication of a 15megabase DNA region in chromosome. Dejerine-Sottas SyndromeNeuropathy hereditary motor and sensory polyneuropathy type III. DejerineSottas syndrome DSS is an early onset demyelinating motor and sensory neuropathy with motor nerve conduction velocities below 12 m s 1The phenotype is genetically heterogeneous and autosomal dominant AD as well as autosomal recessive AR inheritance is described.
Dejerine-Sottas syndrome is a term sometimes used to describe a severe early childhood form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Dejerine sottas syndrome is also called dejerine sottas disease or onion bulb neuropathy or DejerineSottas neuropathy or progressive hypertrophic interstitial polyneuropathy of childhood. Another patient with DejerineSottas syndrome mutation unknown had caloric areflexia in addition to multiple brain stem abnormalities.
29 rows Hypertrophic neuropathy of Dejerine-Sottas Dejerine-Sottas. This syndrome should not be confused with Déjerine syndrome or Déjerine-Roussy syndrome. Clinical symptoms are similar but more severe.
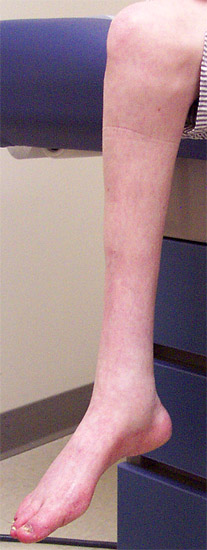
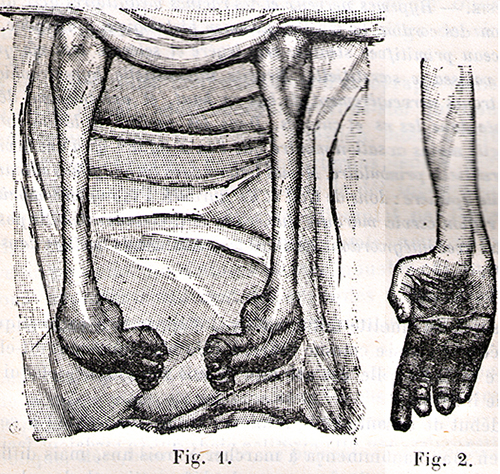
Depending on the specific gene that is altered this severe early-onset form of the disorder may also be classified as CMT1 or CMT4. Dejerine-Sottas syndrome Disease definition A clinical entity that represents a severe phenotype of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease characterized by onset occurring in infancy severe motor weakness delayed motor development extremely slow nerve conduction 10-12 ms areflexia and foot deformity.
Depending on the specific gene that is altered this severe early-onset form of the disorder may also be classified as CMT1 or CMT4.
What are the effectssymptoms of Dejerine-Sottas syndrome. Unlike hearing loss vestibular loss is difficult to identify particularly in a patient presumed to. Dejerine sottas syndrome is also called dejerine sottas disease or onion bulb neuropathy or DejerineSottas neuropathy or progressive hypertrophic interstitial polyneuropathy of childhood. Some patients have generalized hypotonia in infancy. In the context of medical genetics an autosomal dominant disorder is caused when a single copy of the mutant allele is present. Depending on the specific gene that is altered this severe early-onset form of the disorder may also be classified as CMT1 or CMT4. Another patient with DejerineSottas syndrome mutation unknown had caloric areflexia in addition to multiple brain stem abnormalities. 29 rows Hypertrophic neuropathy of Dejerine-Sottas Dejerine-Sottas. Clinical symptoms are similar but more severe.
Unlike hearing loss vestibular loss is difficult to identify particularly in a patient presumed to. 29 rows Hypertrophic neuropathy of Dejerine-Sottas Dejerine-Sottas. Dejerine sottas syndrome strikes the. Dejerine-Sottas neuropathy is a demyelinating peripheral neuropathy with onset in infancy. Clinical symptoms are similar but more severe. Peripheral nerves are the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. Sometimes also described as a subtype III of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive neuropathy.



























Post a Comment for "Dejerine-sottas Syndrome"