Aspirin Coronary Artery Disease
Aspirin coronary artery disease. Aspirin therapy is very helpful for people with CAD or a history of stroke. Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid is an antiplatelet drug used to treat and prevent coronary artery disease. The following groups of patients with established cardiovascular disease or at high risk benefit from aspirin for the prevention of new cardiovascular events.
Coronary Diseasedrug therapy Coronary Diseaseprevention. To determine whether pre-hospitalization use of aspirin is associated with all-cause mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 COVID-19 patients with coronary artery disease CAD. Note that recommendations for aspirin use for the treatment of acute coronary syndrome ACS remain unchanged.
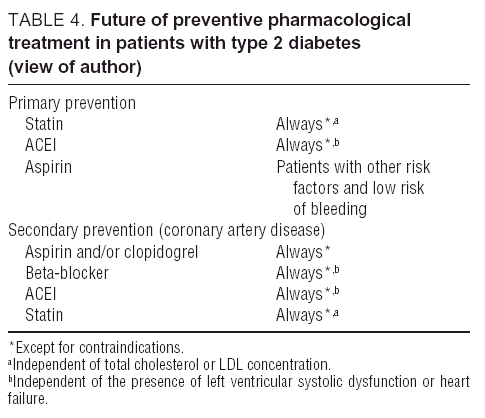
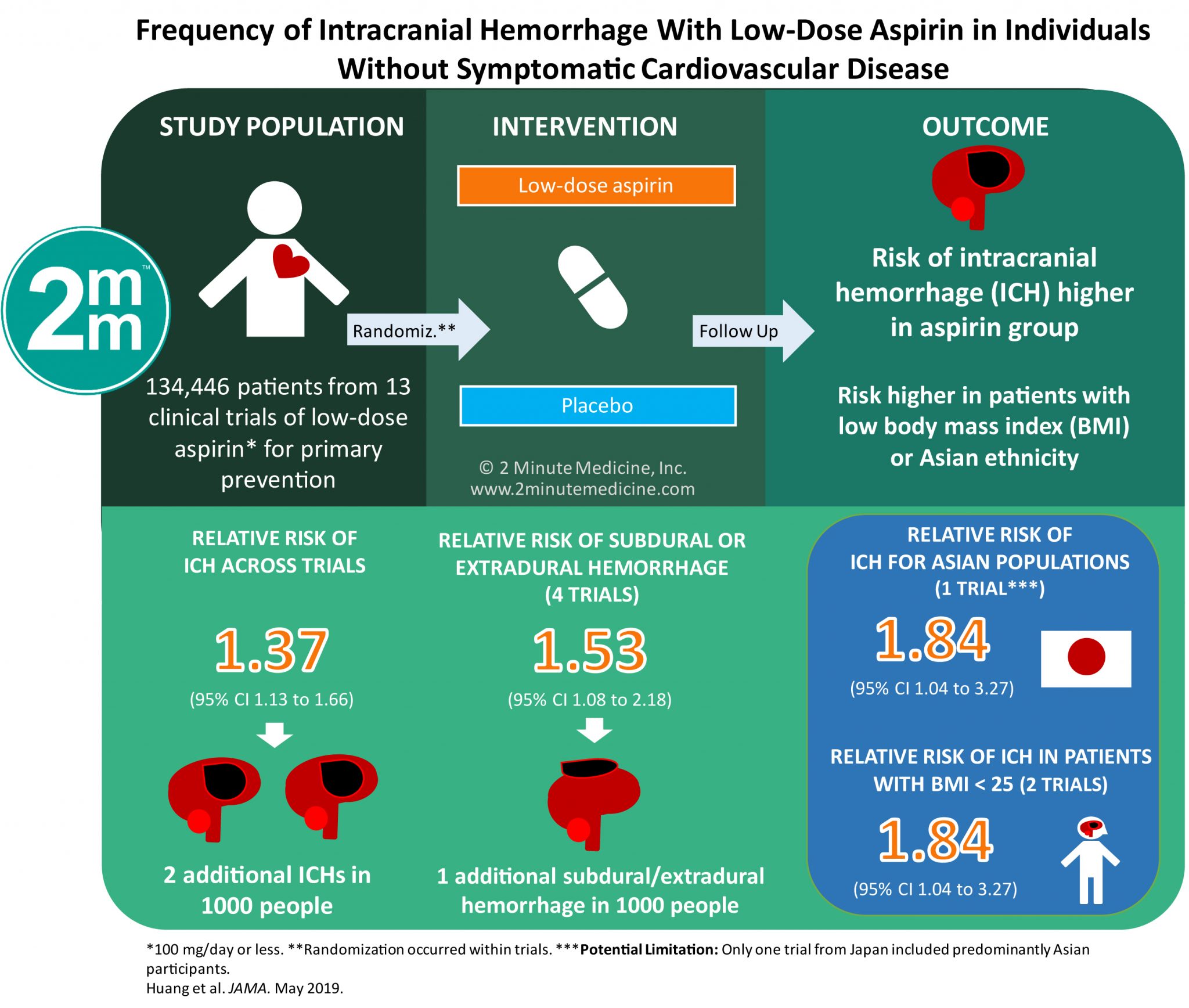
In two randomized placebo-controlled trials in the setting of primary prevention aspirin reduced the incidence of CVD events in individuals homozygous for the GUCY1A3 risk G allele whereas heterozygote individuals. 10 linhas Aspirin is indicated for prevention andor treatment of a wide variety of cardiovascular. Aspirin desensitization can be attempted in patients.
We recruited 183 adult patients with CAD diagnosed with COVID-19 including 52 taking low-dose aspirin mean SD age 69. CCS or stable coronary artery disease CAD is the chronic period from 3-12 months after an index coronary event. Several recent trials have demonstrated diminished or no benefit for aspirin in CCS.
Aspirin or NSAID hypersensitivity is not an uncommon occurrence and can vary from generaliz. Genetic variation at the coronary artery disease risk locus GUCY1A3 modifies cardiovascular disease prevention effects of aspirin. Our study was meticulously performed and is the largest published to evaluate platelet aggregation in coronary artery disease patients on aspirin monotherapy concomitantly treated with PPI.
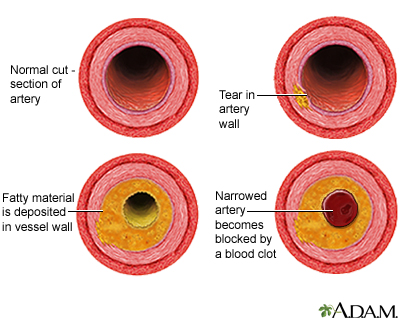
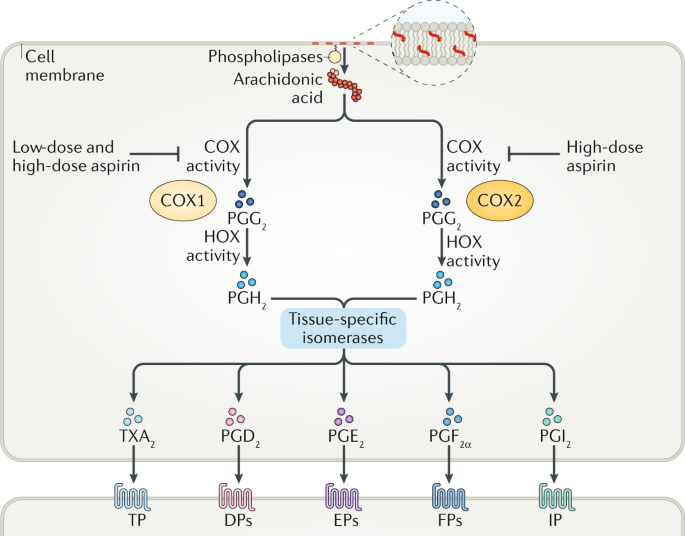
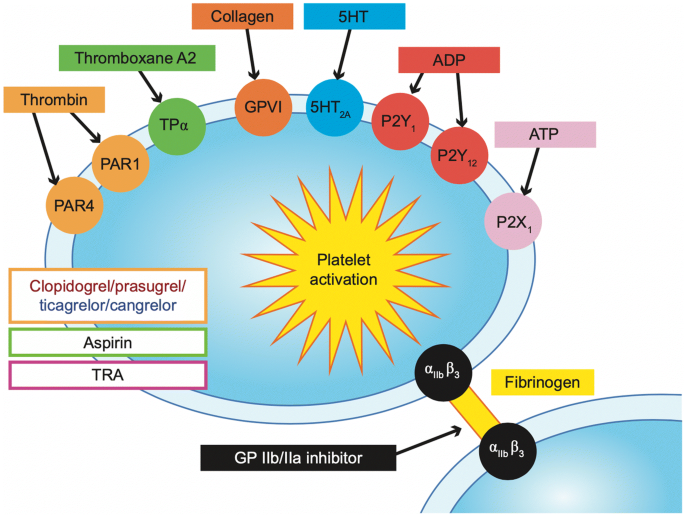
Aspirin is used more frequently than any other drug in the world however it does not inhibit platelet function equally well in all patients. 3 4 Therefore we understand that aspirin acts by reducing the inflammatory component in the atherosclerotic plaques. If you have been diagnosed with CAD your health care provider may recommend that you take a daily dose from 75 to 162 mg of aspirin.
8349998 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types. Effect of aspirin in addition to oral anticoagulants in stable coronary artery disease outpatients with an indication for anticoagulation.
Patients with acute coronary artery syndromes such as acute myocardial infarction MI and unstable angina.
Aspirin therapy is very helpful for people with CAD or a history of stroke. Aspirin desensitization can be attempted in patients. 10 linhas Aspirin is indicated for prevention andor treatment of a wide variety of cardiovascular. CCS or stable coronary artery disease CAD is the chronic period from 3-12 months after an index coronary event. First of all there is evidence that atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease of the vasculature 2 and aspirin intake reduces the levels of inflammatory markers and the risk of vascular events. Aspirin is the most commonly used antiplatelet agent in patients with coronary artery disease CAD. Note that recommendations for aspirin use for the treatment of acute coronary syndrome ACS remain unchanged. 3 4 Therefore we understand that aspirin acts by reducing the inflammatory component in the atherosclerotic plaques. In two randomized placebo-controlled trials in the setting of primary prevention aspirin reduced the incidence of CVD events in individuals homozygous for the GUCY1A3 risk G allele whereas heterozygote individuals.
We recruited 183 adult patients with CAD diagnosed with COVID-19 including 52 taking low-dose aspirin mean SD age 69. Aspirin thins the blood which helps prevent blood clots from forming. Aspirin therapy is very helpful for people with CAD or a history of stroke. If you have been diagnosed with CAD your health care provider may recommend that you take a daily dose from 75 to 162 mg of aspirin. In two randomized placebo-controlled trials in the setting of primary prevention aspirin reduced the incidence of CVD events in individuals homozygous for the GUCY1A3 risk G allele whereas heterozygote individuals. Notably 2 of patients do not receive aspirin therapy because of hypersensitivity. Our study was meticulously performed and is the largest published to evaluate platelet aggregation in coronary artery disease patients on aspirin monotherapy concomitantly treated with PPI.























30738-5.fp.png)













Post a Comment for "Aspirin Coronary Artery Disease"